Suppose we have one peak at 4 260 ppm and another at 4 247 ppm.
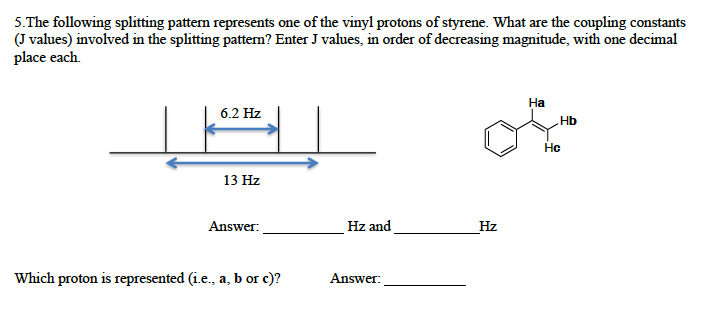
Vinyl coupling constants.
Hydrogens near double bonds are deshielded.
For background information of 1 h nmr you can refer 1 h nuclear magnetic resonance from the last chapter.
Three bonds participate in coupling.
It ranges from 10 18 and denoted by 2 but one condition is applied that the proton present should be non equivalent.
The tables below list coupling constants for a few general cases.
In 1 h nmr spectrum hydrogen atoms bound to a carbon consisting of a double bond these hydrogens are called alkenyl hydrogens are typically found in low field of the nmr spectrum which is the left side and the hydrogens are said to be.
2 j hh 15 10.
There are some 10 lines visible.
With protons bound to sp 2 hybridized carbons coupling constants can range from 0 hz no coupling at all to 18 hz depending on the bonding arrangement.
In a vicinal system of the general type h a c c h b then the coupling of h a with h b j ab must be equal to the coupling of h b with h a j ba therefore j ab j ba.
The implications are that the spacing between the lines in the coupling patterns are the same as can be seen.
The coupling constant j usually in frequency units hz is a measure of the interaction between a pair of protons.
Interestingly the satellites of the vinyl protons 1 j ch 184 2 hz are doublets because the isotopic label now makes the two protons non equivalent and we can detect the coupling between them 6 0 hz.
The first thing to do is convert the peaks from ppm into hertz.
The 2 bond coupling between.
The equation follows the general format of j a b cos θ c cos 2θ with the exact values of a b and c dependent on several different factors.
Coupling constants chem 117 here is the observed spectrum at 90 mhz in cdcl 3 lambert and mazzola pg 101.
Types of coupling constant.
Calculation of coupling constant.
The trick is that j is measured in hz not ppm.
For the simple case of a doublet the coupling constant is the difference between two peaks.
For vinylic hydrogens in a trans configuration we see coupling constants in the range of 3 j 11 18 hz while cis hydrogens couple in the 3 j 6 15 hz range.
The coupling constant is large 5 8 hz when the neighboring units are either ethylene or both racemic vinyl alcohol.
Environment coupling value hz aliphatic h c h geminal.
This type of coupling occurs between protons present on single carbon specifically in the terminal vinyl system.
In general though a plot of this equation has the shape shown in figure 1 4.
The coupling constant between two protons is affected by the dihedral angle between them.
The coupling constant drops to 3 9 hz for any sequence containing at least one meso vv vinyl alcohol dyad which indicates that the average dihedral angle between the methine and hydroxyl protons is different for these sequences.